Three schema Architecture
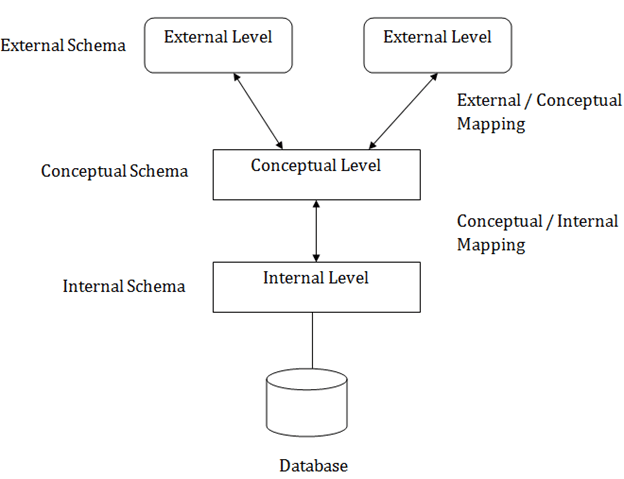

The main objective of three level architecture is to enable multiple users to access the same data with a personalized view while storing the underlying data only once. Thus it separates the user's view from the physical structure of the database. This separation is desirable for the following reasons:
- Different users need different views of the same data.
- The approach in which a particular user needs to see the data may change over time.
- The users of the database should not worry about the physical implementation and internal workings of the database such as data compression and encryption techniques, hashing, optimization of the internal structures etc.
- All users should be able to access the same data according to their requirements.
- DBA should be able to change the conceptual structure of the database without affecting the user's
- Internal structure of the database should be unaffected by changes to physical aspects of the storage.
1. Internal Level

- The internal level has an internal schema which describes the physical storage structure of the database.
- The internal schema is also known as a physical schema.
- It uses the physical data model. It is used to define that how the data will be stored in a block.
- The physical level is used to describe complex low-level data structures in detail.
The internal level is generally is concerned with the following activities:
- Storage space allocations.
For Example: B-Trees, Hashing etc.
- Access paths.
For Example: Specification of primary and secondary keys, indexes, pointers and sequencing.
- Data compression and encryption techniques.
- Optimization of internal structures.
- Representation of stored fields.
2. Conceptual Level
- The conceptual schema describes the design of a database at the conceptual level. Conceptual level is also known as logical level.
- The conceptual schema describes the structure of the whole database.
- The conceptual level describes what data are to be stored in the database and also describes what relationship exists among those data.
- In the conceptual level, internal details such as an implementation of the data structure are hidden.
- Programmers and database administrators work at this level.
3. External Level

- At the external level, a database contains several schemas that sometimes called as subschema. The subschema is used to describe the different view of the database.
- An external schema is also known as view schema.
- Each view schema describes the database part that a particular user group is interested and hides the remaining database from that user group.
- The view schema describes the end user interaction with database systems.
Mapping between Views
The three levels of DBMS architecture don't exist independently of each other. There must be correspondence between the three levels i.e. how they actually correspond with each other. DBMS is responsible for correspondence between the three types of schema. This correspondence is called Mapping.
There are basically two types of mapping in the database architecture:
- Conceptual/ Internal Mapping
- External / Conceptual Mapping
Conceptual/ Internal Mapping
The Conceptual/ Internal Mapping lies between the conceptual level and the internal level. Its role is to define the correspondence between the records and fields of the conceptual level and files and data structures of the internal level.
External/ Conceptual Mapping
The external/Conceptual Mapping lies between the external level and the Conceptual level. Its role is to define the correspondence between a particular external and the conceptual view.
Next Topic DBMS Models

For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]






